Afrihost Network IP NAT Explained
In our continuous efforts to improve security and streamline the efficiency of our network, we have introduced a feature to enhance our defenses against phishing. You will be notified when there is a new login to ClientZone or the Mobile App, particularly after successfully entering an OTP. This approach is designed to help you identify potential security threats, especially those related to the latest phishing scams. By promptly notifying you, we empower you to take quick action, ensuring you can change your password and safeguard your account from unauthorised access. You may also notice notifications about new logins displaying a CG NAT IP.
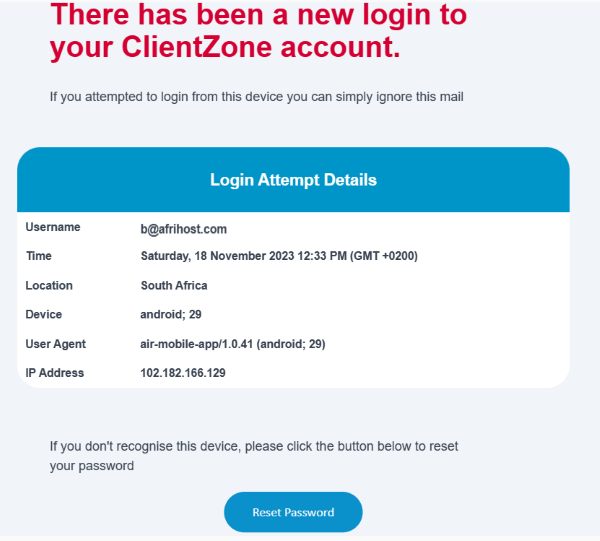
To provide clarity on these updates, we will go through these concepts and explore the following in detail:
- What is NAT
- What is CG NAT
- What is a public IP Address
- What is a private IP Address
- Why is my public IP address different from my private IP address
An IP or Internet Protocol address is a numerical identifier assigned to each device that connects to the Internet. IP addresses allow devices to talk to each other and exchange information.
IPv4 addresses are made up of four sets of one to three-digit numbers,
IPv6 uses eight groups of four hexadecimal digits, separated by colons.
An example of IPv4 - 104.20.31.244
An example of IPv6 - 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:73b4
What is NAT
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a technology used in routers to enable multiple devices within a local network to share a single public IP address when communicating with external networks, such as the Internet. NAT plays a crucial role in addressing the limitations of IPv4, the Internet Protocol version 4, which has a limited pool of globally unique IP addresses.
How NAT works and why it is important:
- Address Translation: When devices within a local network (private network) communicate with the internet, they use private IP addresses. These private IP addresses are not routable on the global internet. NAT translates these private IP addresses into a single public IP address assigned by the Internet Service Provider (ISP).
- Conserving Public IP Addresses: NAT allows multiple devices in a private network to share a single public IP address. This conserves the limited pool of available public IP addresses, as many devices can access the internet using a smaller set of globally unique addresses.
- Types of NAT: There are different types of NAT, such as
- Static NAT: Maps a specific private IP address to a specific public IP address.
- Dynamic NAT: Maps private IP addresses to public IP addresses from a pool of available addresses.
- NAT Overload (or PAT - Port Address Translation): Maps multiple private IP addresses to a single public IP address using different port numbers. This is the most common form of NAT and is often referred to as "many-to-one" NAT.
- Port Numbers: NAT uses port numbers to keep track of multiple simultaneous connections from different devices sharing the same public IP address. Each device within the private network is assigned a unique port number, allowing the NAT device to correctly forward incoming data to the appropriate device.
- Enhanced Security: NAT provides a level of security by hiding the internal structure of a private network. Devices with private IP addresses are not directly accessible from the internet, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- IPv6 Transition: While NAT has been widely used to mitigate the IPv4 address exhaustion issue, the adoption of IPv6 (the next-generation Internet Protocol) aims to provide a vast number of unique addresses, reducing the reliance on NAT. However, IPv6 adoption is still in progress.
What is CG NAT
Carrier-Grade Network Address Translation (CG NAT) is an extension of traditional Network Address Translation (NAT) technology that is implemented at the service provider or carrier level. CG NAT allows multiple customers (subscribers) to share a single public IP address, helping service providers manage the limited availability of IPv4 addresses as more devices connect to the internet.
Key features of CG NAT:
- Shared Public IP Addressing: CG NAT enables service providers to share a pool of public IP addresses among multiple subscribers. Each subscriber is assigned a private IP address within their home or business network, and these private addresses are then translated into a smaller set of public IP addresses when communicating with external networks.
- Address Conservation: One of the primary motivations behind CG NAT is to conserve the limited pool of available IPv4 addresses. As the demand for internet-connected devices continues to grow, the number of available IPv4 addresses has become insufficient, and CG NAT helps address this scarcity by allowing multiple users to share a smaller set of public IP addresses.
- Port Multiplexing (Port Address Translation - PAT): CG NAT typically employs Port Address Translation (PAT), also known as port multiplexing or overloading. PAT maps multiple private IP addresses to a single public IP address using different port numbers. This allows for a large number of simultaneous connections from multiple users to be distinguished and managed using a single public IP address.
- Challenges and Limitations: While CG NAT addresses the immediate need for IPv4 address conservation, it introduces certain challenges. For instance, it can pose difficulties for certain applications or services that rely on unique public IP addresses, such as online gaming, video conferencing, or peer-to-peer applications.
- IPv6 Adoption: In the long term, the internet community is moving toward the adoption of IPv6, which provides a much larger pool of unique IP addresses compared to IPv4. As IPv6 deployment progresses, the need for CG NAT is expected to diminish.
- Impact on End Users: From an end-user perspective, the use of CG NAT may result in some limitations. For example, users may experience issues with certain online applications that expect a unique public IP address. Additionally, troubleshooting network issues may be more challenging when multiple users share the same public IP.
What is a public IP Address
A public IP address is like a unique identifier for your home or business on the internet. Imagine your home having a specific address that distinguishes it from others in the neighbourhood. Similarly, a public IP address serves as the address for your internet connection, allowing other devices and servers on the internet to find and communicate with your network.
What is a private IP Address
A private IP address is an IP address that is reserved for use within a private network and is not directly accessible from the internet. Private IP addresses are used to identify devices within a local area network (LAN), such as those in your home or office. They are defined by specific ranges as outlined in the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) Request for Comments (RFC) 1918.
Why is my public IP address different from my private IP address
Your public IP address is different from your private IP address due to the structure of the Internet and the way networks are organized.
Let's break down the reasons for this distinction:
- Global Addressing: Public IP addresses are part of a globally unique addressing scheme. Each device connected to the internet needs a unique identifier so that data can be sent to and received from the correct destination. Public IP addresses are assigned by your Internet Service Provider (ISP) and are unique on the global internet.
- Private Network Addressing: On the other hand, private IP addresses are used within local networks (like your home or office). These addresses are not unique globally and can be reused in different private networks. Private IP addresses are reserved and not routable over the internet.
- Network Address Translation (NAT): Most homes and small businesses use a router to connect multiple devices to the internet. These devices typically have private IP addresses within the local network. The router performs Network Address Translation (NAT), which allows all devices in the local network to share a single public IP address when communicating with external servers on the Internet.
- Address Space Conservation: Private IP addresses are used to conserve the limited pool of available IPv4 addresses. With the increasing number of devices connected to the internet, private IP addresses help manage the scarcity of globally unique IPv4 addresses. IPv6, a newer addressing scheme, aims to provide a vast number of unique addresses and reduce reliance on private addressing, but widespread adoption is still in progress.
- Security: Keeping private and public IP addresses separate enhances network security. Devices with private IP addresses are shielded from direct exposure to the internet, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. The router acts as a barrier, and only the router's public IP address is visible to external networks.
Please read Password security Help Centre article to learn more.
If you would like to know more about Email phishing and spoofing, please read our Help Centre article for further information.
If you need further assistance, please connect with our friendly support via Afrihost Help Support Channels.

